Description
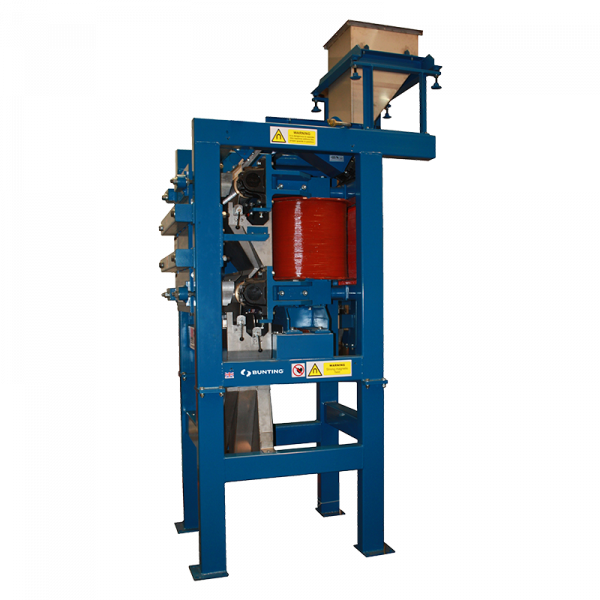
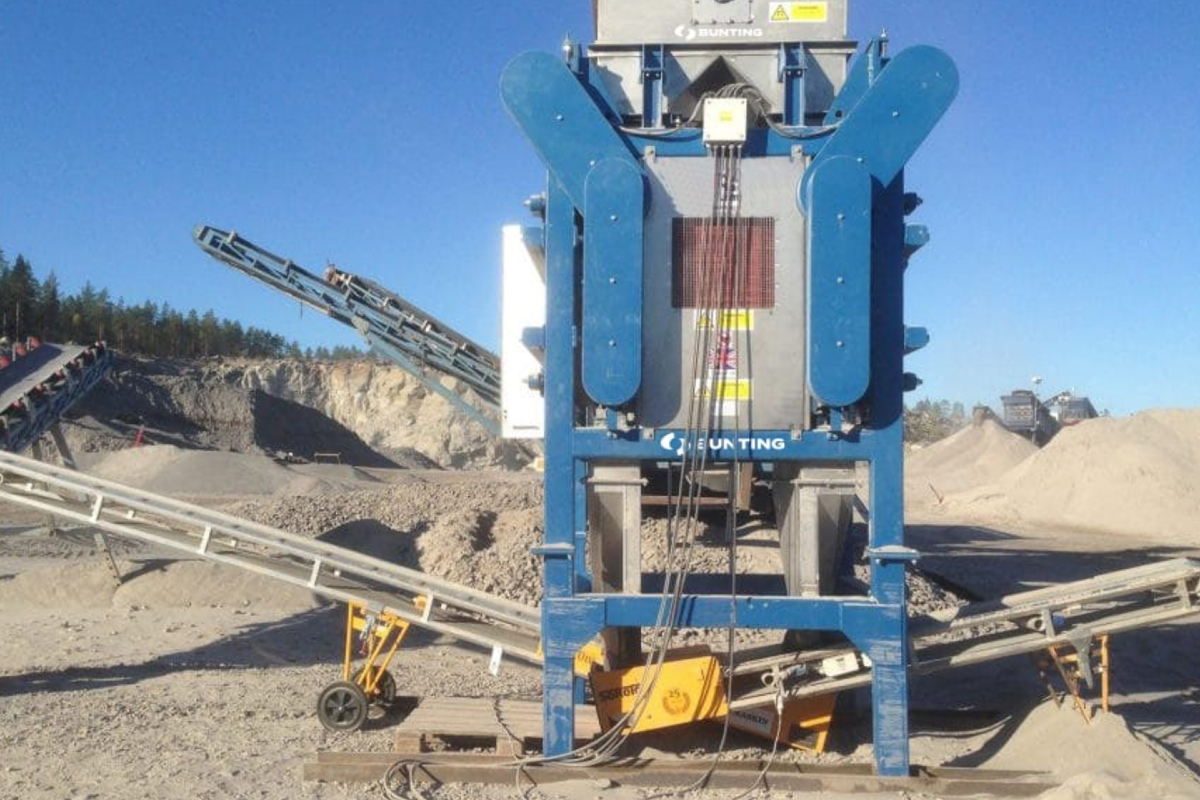
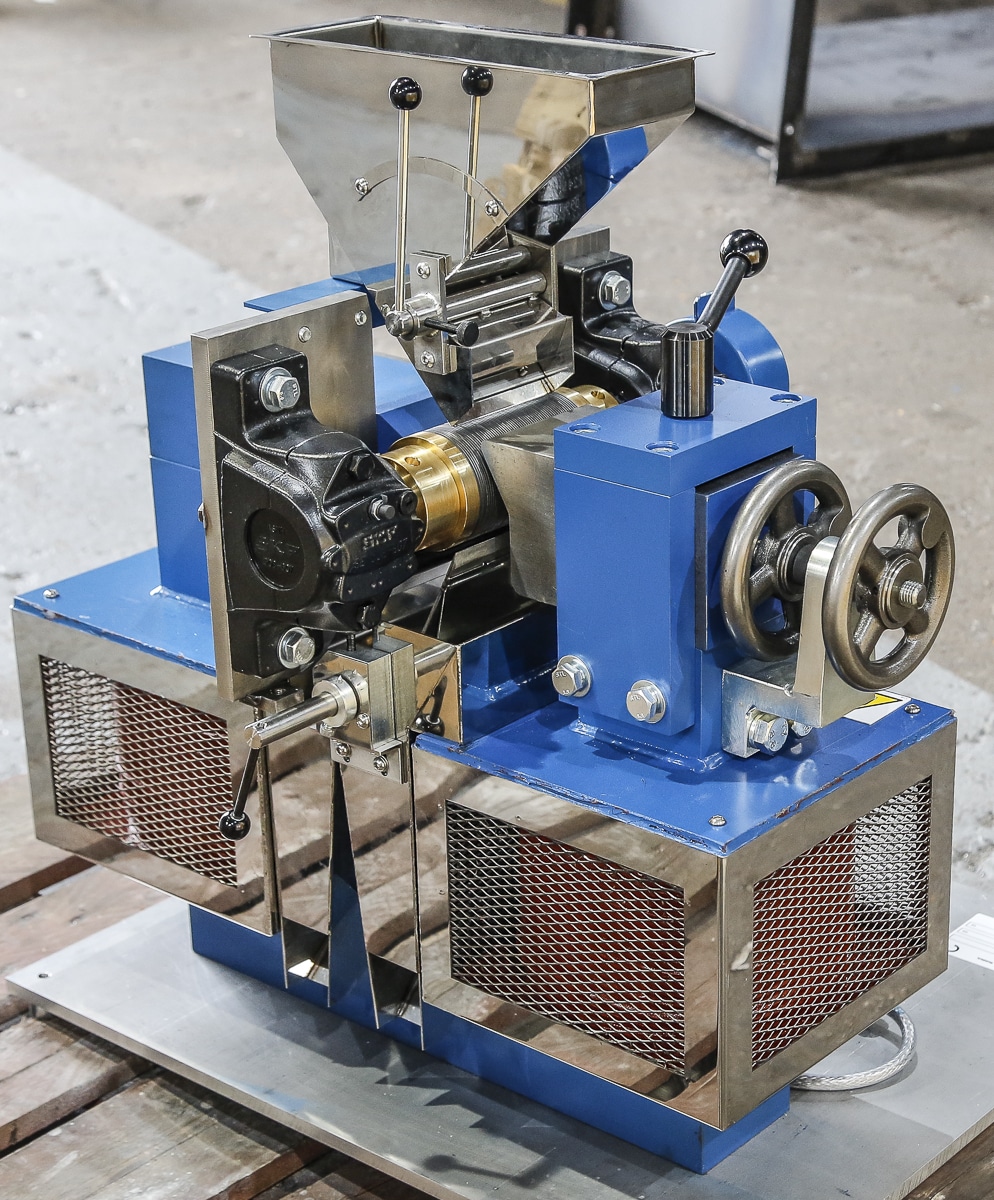
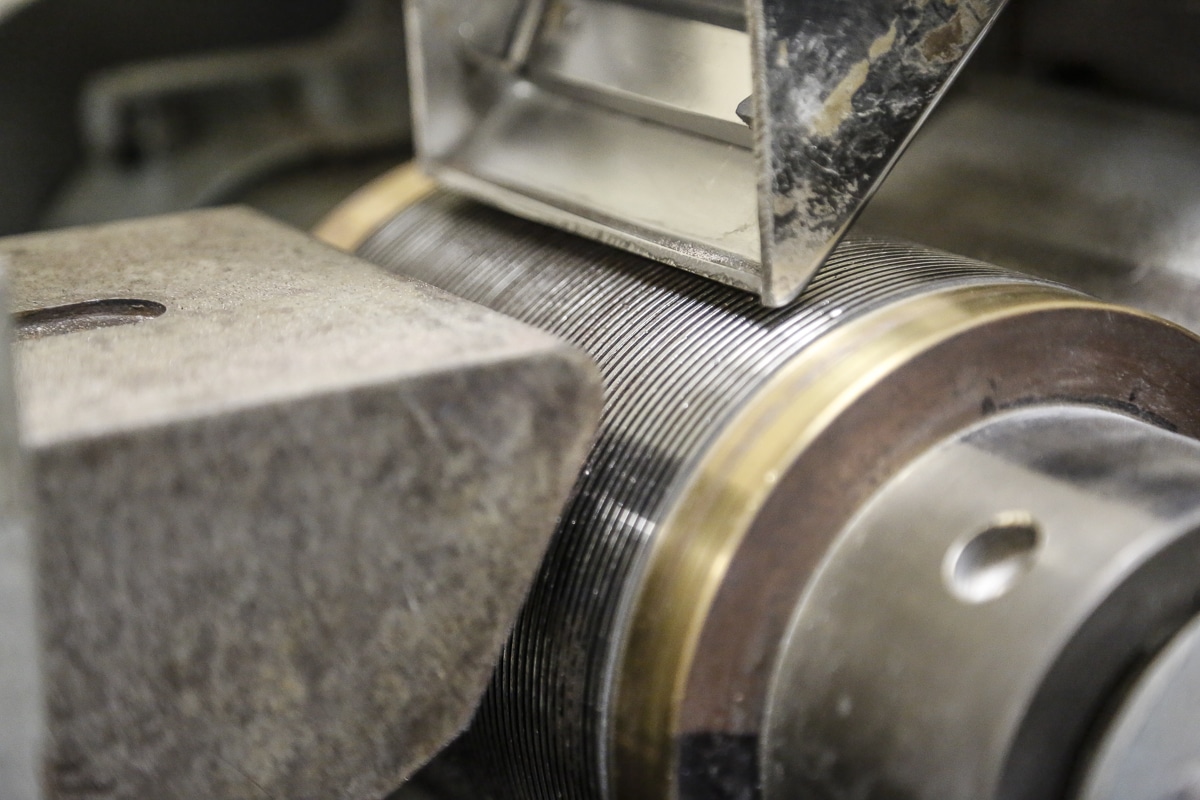
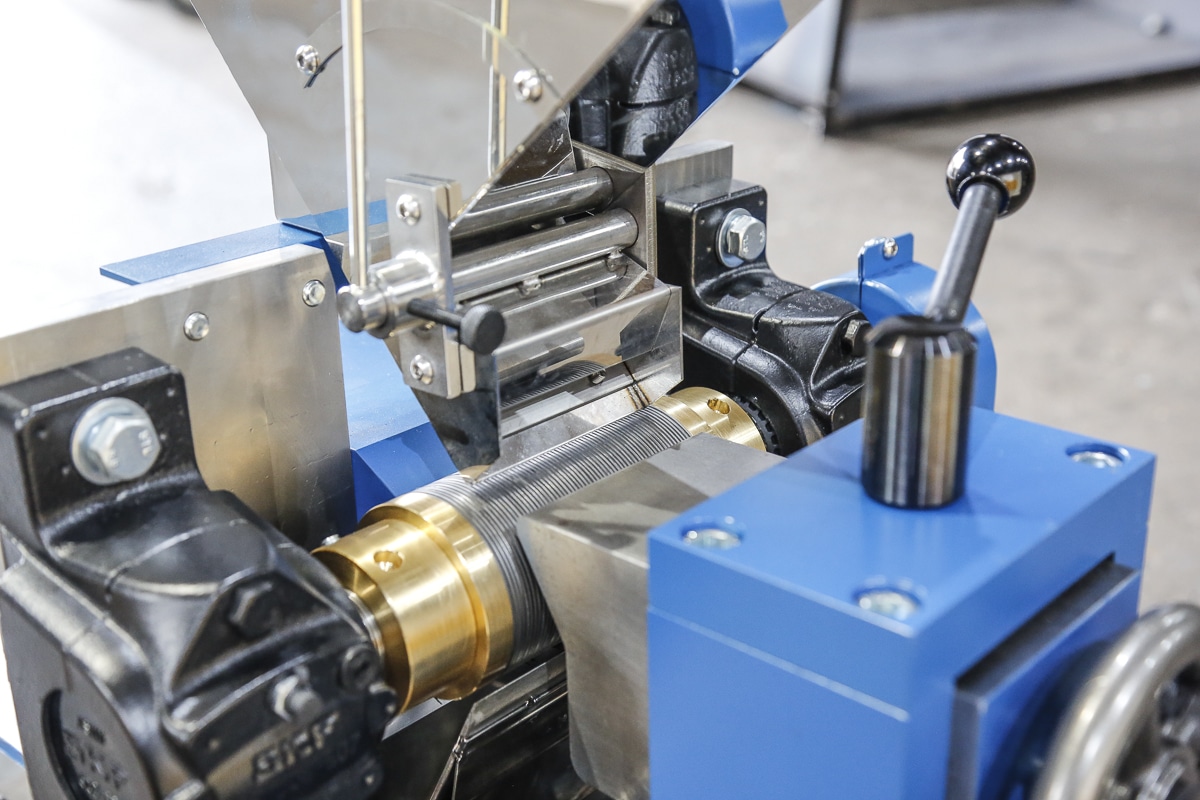
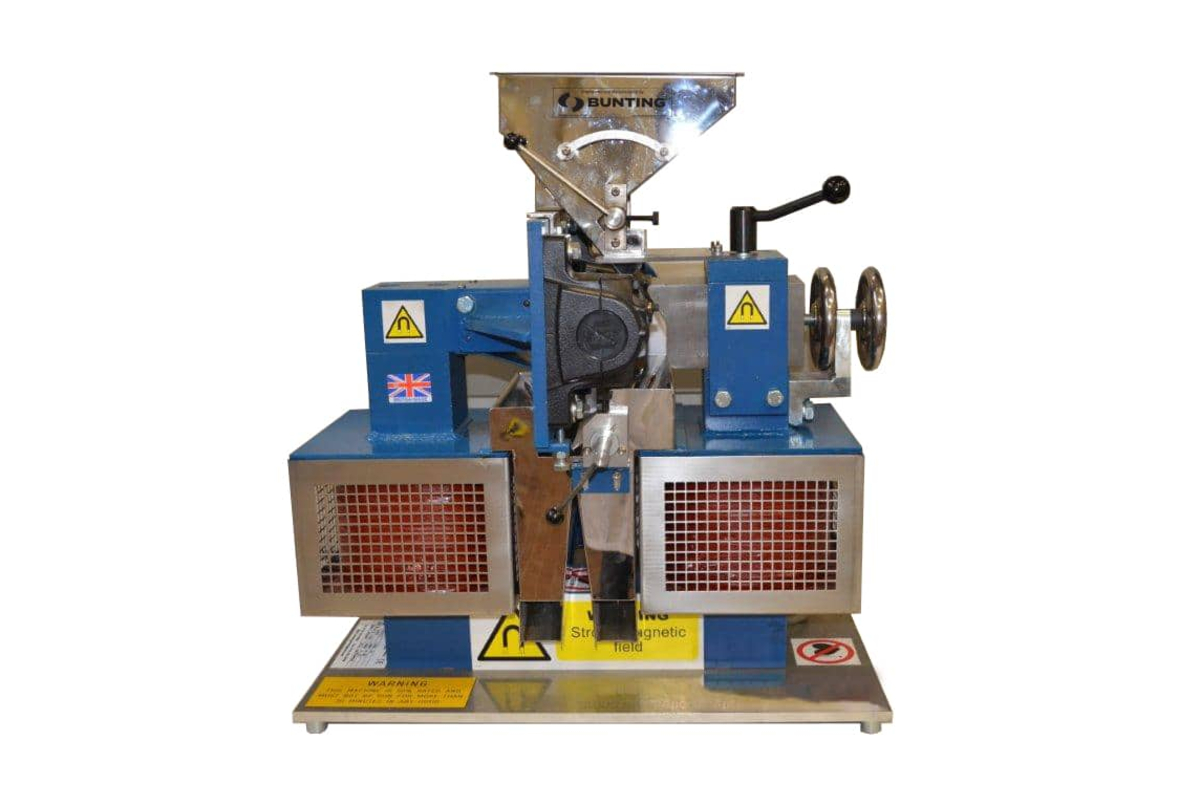
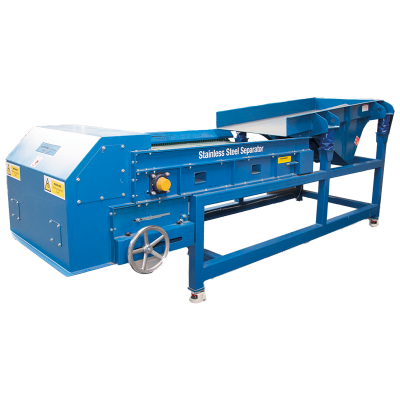
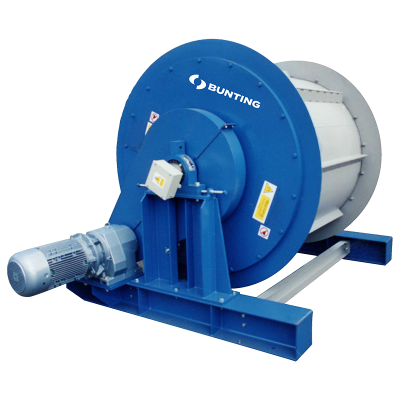
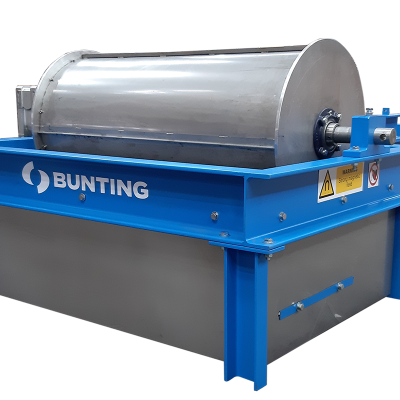
The Induced Roll Magnetic Separator (IRS) is a proven technology for purifying dry non-metallic minerals used in the ceramics and glass industries and recovering fine, weakly magnetic particles in recycling. The IRS uses electromagnetically generated high-intensity magnetic fields to continuously separate small paramagnetic particles from materials with a particle size range of -2mm to 45 microns. The IRS comprises an electromagnetically induced steel roll positioned between a bridge bar and a pole piece. The peak magnetic field generated on the induced roll is 2.2 Tesla (22,000 Gauss).
The IRS offers many advantages compared with permanent magnetic separators, including:
- Adjustable features include:
- Magnetic field strength, by varying the power to the electromagnetic coils;
- Roll speed for retention time of the mineral in the magnetic field;
- The gap between the Induced Roll and Pole to accommodate different feed size ranges;
- Ability to process hot mineral feeds (up to between 80 and 100 C)
- Generates limited static charge that may affect the separation performance
- Robust design that requires limited maintenance and spare parts
Related blogs
- Video Explanation of the Induced Roll Magnetic Separator IRS
- Rare Earth Roll or Induced Roll Magnetic Separator
Operation
In operation, a controlled rate of material (e.g. non-metallic minerals) is fed from a hopper or vibratory feeder onto the rotating induced magnetic roll (roll speeds vary between 80 to 120 RPM). Weakly magnetic material is attracted, deflected, or held to the roll surface. The trajectory of the non-magnetic material is unhindered, discharging away from the separated material. Captured magnetic material discharges from the roll at a point of lower magnetic intensity, often aided by a brush. A splitter plate is interposed between the two product streams for a clean separation. The IRS is often set to produce a ‘middlings’ stream (i.e. very weak magnetic material mixed with non-magnetics) by adding a second splitter plate. It is common practice to have two induced rolls mounted in series on the same unit to enable a double pass for improved separation efficiency and process performance.
Applications
The Induced Roll Magnetic Separator is widely used across the non-metallic minerals, ceramics and glass industries and is increasing in the recycling sector for specialist material separation.
In mineral processing, typical capacities for a metre-wide unit vary based on the mineral type, density and particle size distribution and are ideally determined by laboratory test trials. Typical capacities per meter width are:
- Concentration of ilmenite sands: 4tph
- Chromite concentration: 3-5tph
- Silica sand upgrading: 2-3tph
Bunting has supplied the IRS to mineral companies processing a wide range of minerals, including:
- Apatite
- Baddeleyite
- Barite
- Calcite
- Cassiterite
- Corundum
- Feldspar
- Flint Clay
- Glass Sands
- Kyanite
- Limestone
- Manganese
- Mica
- Mullite
- Nepheline Syenite
- Petalite
- Quartz
- Rutile
- Scheelite
- Silicon Carbide
- Spodumene
- Wollastonite
- Zircon